GAMES104-NOTE3
1. 游戏引擎的工具链-基础
1.1 总览
在商业引擎中实际工具链的开发是多于引擎本身的
基本Foundation of Tool Chains
• What is Game Engine Tool Chains
• Complicated Tool GUI
• How to Load Asset - Deserialization
• How to Make a Robust Tools
• How to Make Tool Chain
• What You See is What You Get (WYSIWYG)
• One More Thing - Plugin
工具链更大的意义在于调合游戏开发各个环节的人的思维模式。
那这么一个庞大的系统的话,最外的基础我们叫做DCC(Digital Content Creation,比如3DMax、Maya、ZBrush、PS、Houdini大量第三方软件产生资产和素材),通过游戏的工具链,进入我们整个游戏的Pipeline。这里有个术语叫做:ACP(Asset Conditioning Pipeline),工具链就在ACP这一层
1.3 工具链的GUI
对于GUI模型,分两大类的实现方式
-
Immediate Mode
每一帧由游戏逻辑直接告诉渲染去画上去。
缺点是逻辑方面业务压力大,扩展性不好, -
Retain Mode
当我要画一些UI的时候,我并不是直接画到屏幕上去,我先说我要画一个Box,大小、尺寸等,把这些信息一个个交给类似Graphics中的Command Buffer一样,将所有的指令全部存储在这里,到了GUI自己绘制的逻辑之后自己根据已经存储的指令,自己去画了。好处就是游戏的逻辑,与工具的GUI分开了,这个模型扩展性强、性能好,还有一点就是如果你不改变它,你就不需要更新它的指令,这也是非常符合游戏架构的理论模型
如QT GUI, Unreal UMG, WPF GUI
1.4 工具链GUI的Design Pattern
对于Retain Mode的GUI实现,需要结合 DP进行才能保证扩展和持续性。
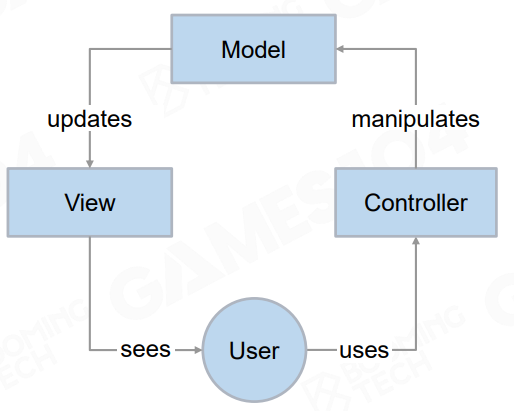
- MVC模式:1978年创建
Model: The central component of the
pattern, responsible for managing the data
of the application.
View: Any representation of information
such as a chart, diagram or table.
Controller: Accepts input and converts it to
commands for the model or view.
将数据流清晰化了,Model单向的到View,View不能反过来写Model,所以可以理解为Model将数据输送给View了,但是Model本身并不会被弄脏,但是如果你想修改Model中Logic的数据的话,只能通过Controller,它能进行各种处理、过滤,然后去修改你的Model,这样一个环流的结构(因为已经变成了单形线),很清晰,容易切断和管理
WEB前端有很多用处
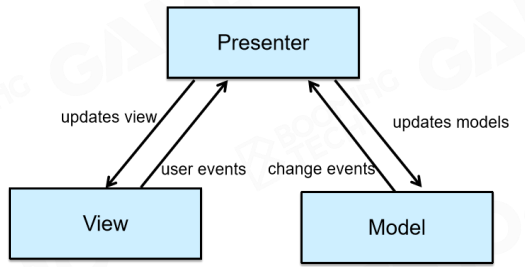
- MVP
MVP实现了把View与Model隔开,完全不知道model的存在!
把所有的复杂度转到Presenter方。
Model: An interface defining the data to be displayed or otherwise acted upon in the user interface.
View: A passive interface that displays data (the model) and routes user commands (events) to the
presenter to act upon that data.
Presenter: Acts upon the model and the view. It retrieves data from repositories (the model), and
formats it for display in the view.
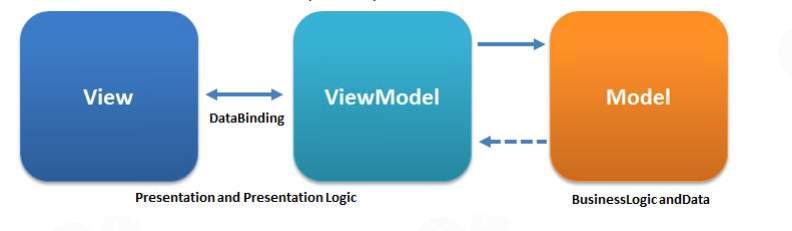
- MVVM
与MVP类似也把View与Model分开,使用一个ViewModel东西,建立一个DataBinding机制。
View与一个独立的xml文件的方式,把需要的绑定和UI完善出来。程序员实现ViewModel和Model.
View: using a WYSIWYG tool such as Dreamweaver,VS Blend and save as html/xaml , view state
that MVC encodes in its View classes is not easy to represent.
Binding: bind View Data to the Model ,no more code in View classes.
ViewModel - Model of View: The Model is very likely to have a data types that cannot be mapped
directly to controls,ViewModel contains data-transformers that convert Model types into View types.
缺点: data-binding的调试不易,对于小型UI过于繁重了。
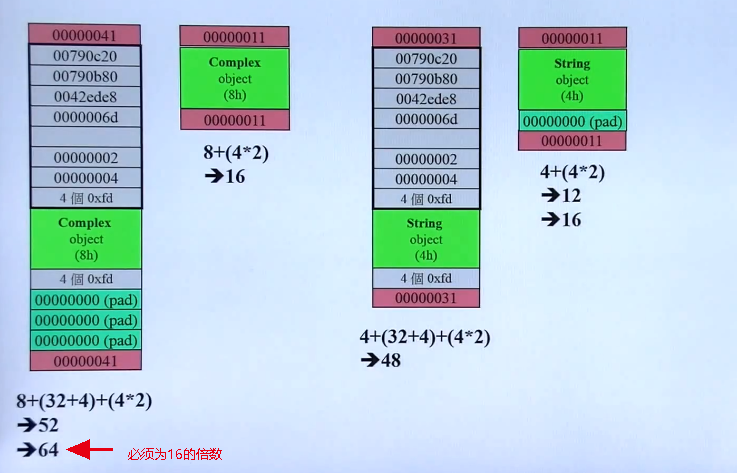
1.5 序列化与反序列化
Serialization 存出去,把数据变成一个二进制块。
is the process of translating a
data structure or object state into a format
that can be stored (for example, in a file or
memory data buffer) or transmitted (for
example, over a computer network) and
reconstructed later.
** Deserialization** 把二进制解成一个数据结构
is the opposite operation,
extracting a data structure from a series of
bytes.
1.6 序列化
那如何把数据SAVE起来?
-
Text Files: 使用Text文本格式的文件来存储
如Json, YAML, XML等。 Unity Editor使用YAML。 CryEngine使用XML/Json -
Binary Files
保存数据为二进制流,需要额外的工具进行读和取。
Unity Runtime, Unity Editor (optional)
CryEngine (optional)
Unreal: UAsset
对比两种文件,二进制小非常多,且加载更快。Text Files更适合做为debug。
-
资产引用
资产引用是一种去除大量重复资源数据的方式,通过查找依赖关系的方式 -
资源实例
Data instance is a way to create a parent data that you can use
as a base to make a wide variety of different children and can
also be used directly
那如何定义每个实例的特性呢?
- 资源实例变体:
如果一个model的material各个地方不同,那这里可以使用实例变体的方式 - 资源数据继承
如果只有变体,可能还是会有大量的冗余部分,这里可以使用继承的特性
1.7 反序列化
如何把数据LOAD出来呢?
并不能一上来就全部读出来,而是需要解析一个个语义。
就如XML,对于游戏引擎的数据来说,解析就先得构建一个树状结构
这样的树状结构,实际就是Asset底层结构。
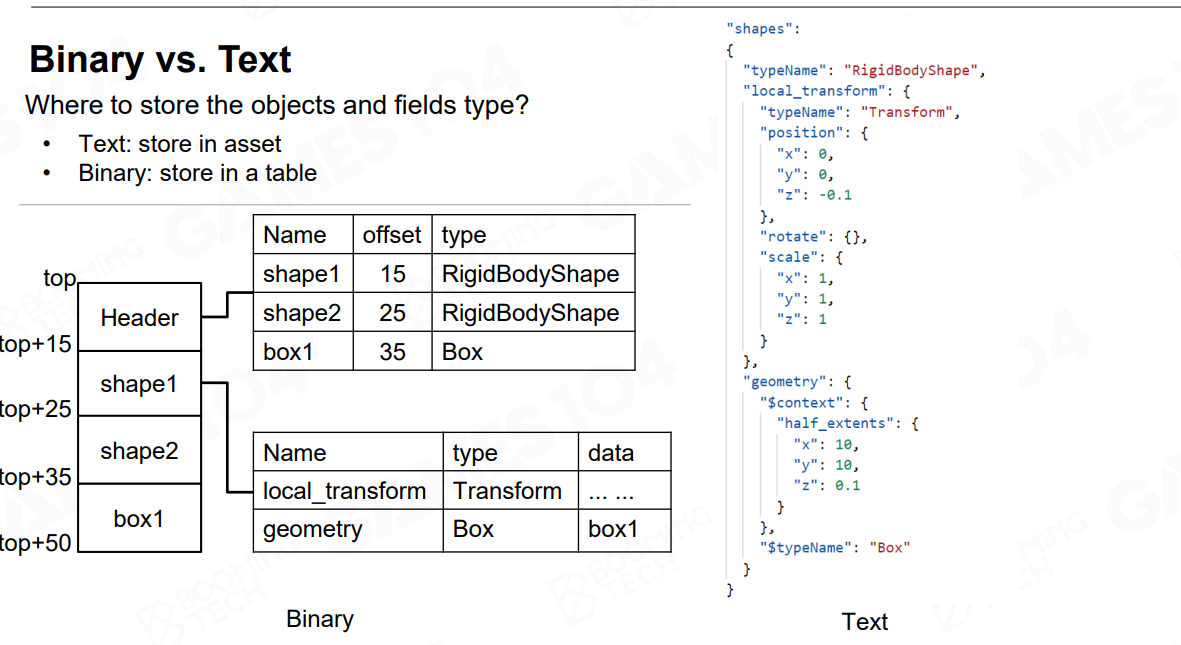
- Endian
用二进制做反序列化时,需要注意这个Endian
同样结构,是把大byte放前面还是小byte放后面?
Big Endian:
begin with most significant byte
end with least significant byte
Little Endian:
begin with least significant byte
end with most significant byte
Processor Endianness
PowerPC (PPC) Big Endian
Sun Sparc Big Endian
IBM S/390 Big Endian
Intel x86 (32 bit) Little Endian
Intel x86_64 (64 bit) Little Endian
ARM Bi (Big/Little) Endian
1.8 兼容性问题
Unreal的处理方案:
为每一个资产有一个定义好的版本号(手写),如果数据没有,则塞一个default value,如果是多余数据,则跳过
Google的做法
protocol buffers:unique number for field
为每一个数据属性维护一个ID,在数据更新时只需要比较这个ID是否变化。
Serialization:
- For every field, generate a “key” (fixed size) according to
its field number and type. - Store field data with key, key is stored in the first few bytes.
Deserialization: - Field not in schema but in data:
key would not be recognized, skip the field. - Field in schema but not in data: set default value.
1.9 构建Robust Tools
更健壮的工具
- Undo/ redo
最核心的功能!! - Crash 自动存盘
1.10 Command模式
针对1.9的需求,将操作原子化为Command。
建议应该在工具链的早期引入Command
Command原子化最经典的结构: UID,数据,操作/反操作, 序列化/反序列化
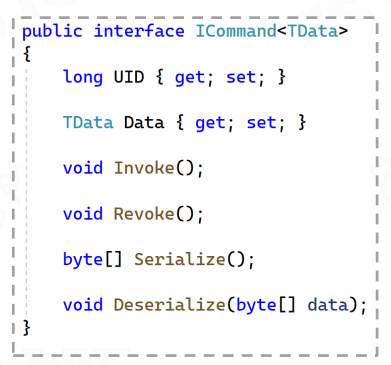
核心三类Command:
- Add
• Data: Usually data is a copy of the runtime instance
• Invoke: Create a runtime instance with data
• Revoke: Delete the runtime instance - Delete
• Data: Usually data is a copy of the runtime instance
• Invoke: Delete the runtime instance
• Revoke: Create a runtime instance with data - Update
• Data: Usually data is the old and new values of the modified properties of the runtime instance and
their property names
• Invoke: Set the runtime instance property to the new value
• Revoke: Set the runtime instance property to the old value
1.11 Data Schema
当针对不同的用户会有不同的工具,因此也有情况是相同的数据,对于不同的用户会表现为不同的工具。
解决这类问题,需要把工具的数据进行细化,用统一的描述和定义,这样可以适配到不同的工具。
这里引入Data Schema来描述一个数据
A data schema is the formal description of the structures your system is working with.
-
Schema基本元素:
Abstraction of the basic building block of the world
• Atomic Types: Int, Float, Double …
• Class Type: Use atomic types to present complex data structure
• Containers: Array, Map … -
继承的特性
数据间需要对相互之间及类型的继承,这样可以派生出各种变种和引用。 -
定义Schema的方式
- 使用独立的schema定义文件
问题:
需要一个自定义的代码转换器,这个转换器在使用过程中会出现迭代,报错等问题。
对于行为的定义的不方便,这一点在方法2中得到解决。 - 定义在文件中
问题:
稳定性需要尤其重要,虽然可以定义行为,但是缺点是容易在定义schema时崩溃。

1.12 引擎数据
三种方面:
Runtime View: 关注更快的读取,更高效的处理
Storage View: 节约空间,更快的写入速度
Tools View: 更方面理解的显示,编辑的便利性(一个虚拟的存在,由工具的UI实现)
1.13 Tools View
工具设计的核心是如何去处理好这个Tools View
- Understandable
- Various Editor Modes,自由适配的编辑器显示(高级与基础模式)
1.14 WYSIWYG
所见即所得
工具链的构建方式:
-
Stand-alone Tools
把工具链的代码独立开,保证引擎的纯净
缺点:难以实现WYSIWYG -
In Game Tools - 推荐
在引擎Runtime的基础上构建工具链
Pros
• Access to all engine data directly
• Easy to preview the game in the editor
• Easy to make live in-game editing
Cons
• Complex engine architecture
• Requires a complete engine UI system to make
the editor UI
• When the engine is crashing, the tools become
unusable as well
1.15 PIE
Play in editor
直接在editor下就能play
两种实现方式:
-
Play in editor world
Pros
• Easy architecture tools layer
• Quick state change
Cons
• 数据混乱的问题Game mode may cause data changes
• 出现数据在editor下没问题,但runtime有问题
Example
• Piccolo -
Play in PIE World
把游戏数据复制一份,独立运行
Unreal的模式
Pros
• Data separation
• Easy to instantitate multiple game instances
Cons
• Architecture complex
1.16 Plugins
工具链也需要支持Plugin插件系统
现代引擎重要的开发能力展现。
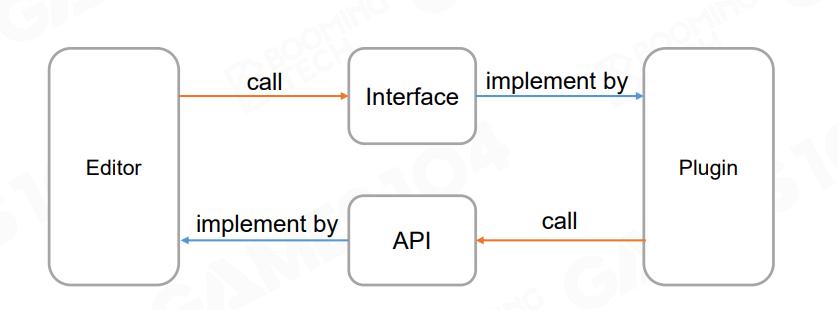
要求尽可能把功能API化,这样更方便实现扩展性需求,为插件调用打好基础。
2. 游戏引擎的工具链-高级
2.1 总览
Applications & Advanced Topic
•Glance of Game Production
•Architecture of A World Editor
•Plugin Architecture
•Design Narrative Tools
•Reflection and Gameplay
•Collaborative Editing
2.2 Glance of Game Production
- 现代引擎工具链的挑战:
- 海量不同的数据
- 不同角色的思维方向
- WYSIWYG 的实现复杂度
2.3 Architecture of A World Editor
以UE为例
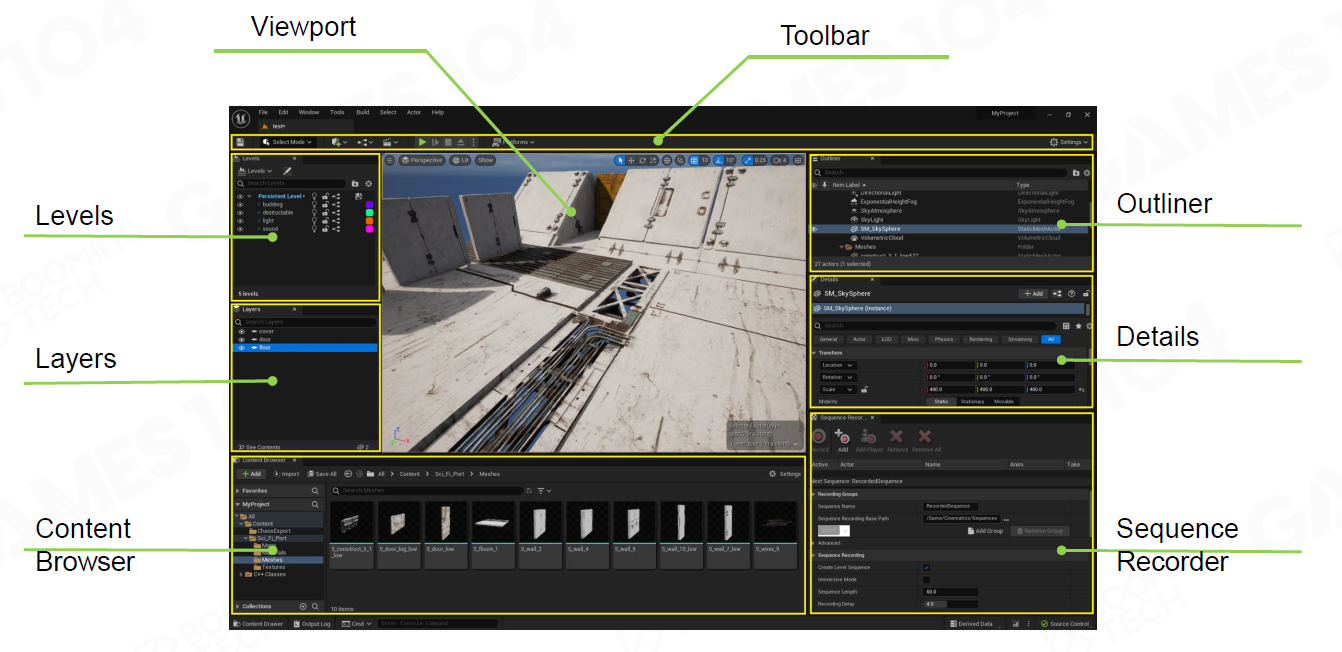
- Editor Viewport
• 与用户关联的主窗口 Main window of interaction between designers and game world
• 一个编辑模式的游戏 Powered by a full game engine in special “editor” mode
• 提供一系列的工具和编辑 Provides a variety of special gadgets and visualizers for editing
注意EditorOnly的代码的安全性问题
- Editable Object
- 把游戏中的对象做为Editable
- 对不同的对象设计不同的编辑view
- 数据通过Schema自动反射生成编辑器界面
-
Content Browser
资产管理器
对于UE来说,这里可能实现跨项目共享资源 -
Mouse Picking
鼠标选取
实现方案:
- Ray Casting
实际使用的一个物理引擎
缺点是性能不好,选择前后物体需要特殊处理(添加object id,以framebuffer取到对应的方式)。但优点是不需要cache,支持选中多个物体 - RTT
Pros:
•Easy to implement range queries
•Ability to complete queries quickly
Cons:
•Need to draw an extra picture
•Obstructed objects cannot be selected
-
Object Transform的编辑
-
Terrain - Height Brush, Instance Brush(对对象进行实例化,但在大场景中对内存要求较高),自定义笔刷的功能
-
Environment
困难点:对于不同的环境,sky, terrain之类,应该有一套规则, 如铺路面,要满足地形路的高低
这里引入一个Rule System: 对于不同的环境需要给予一定规则。
2.4 Plugin机制
任何的系统和对象类型都需要为一个编辑器的插件
几种多Plugin的构建模型
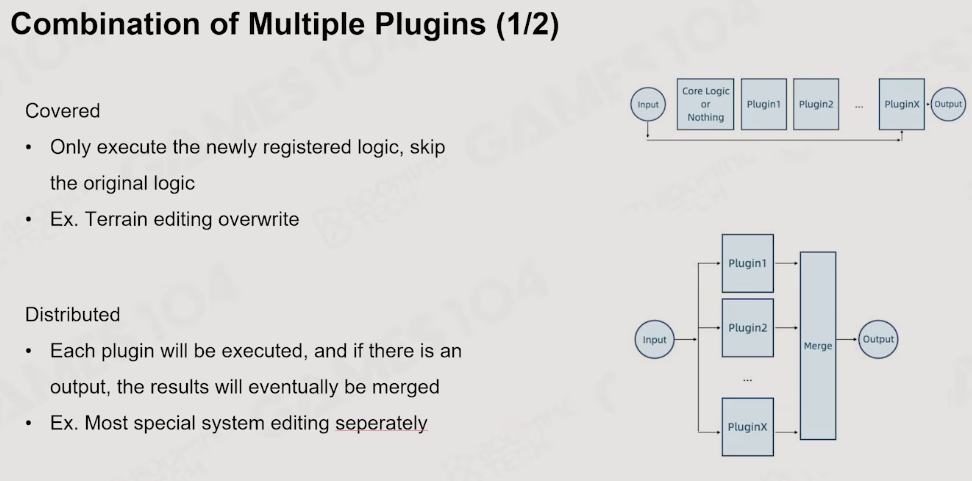
以pipeline形式的构建则是一个前一个输出为后一个输入的方式
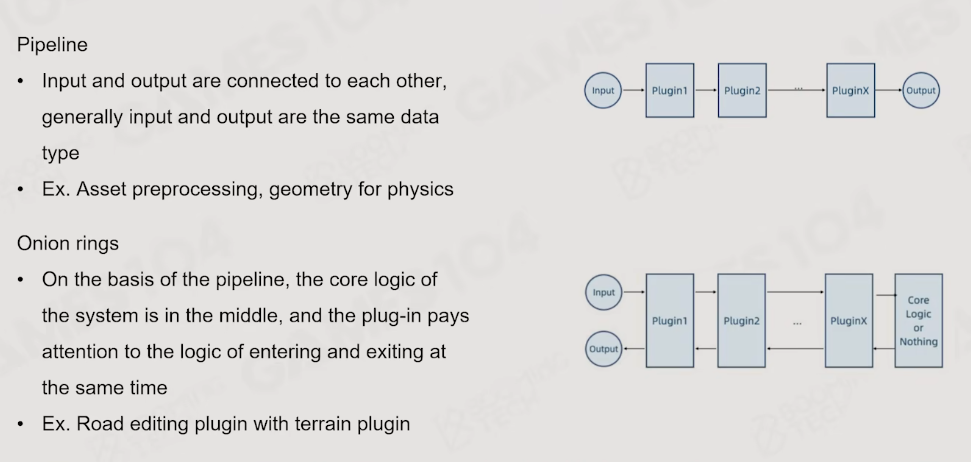
2.5 Timeline
如Unreal中使用Sequencer的方式以每条Track规划每个对象的行为。
用时间帧来处理,如剧情,声效,UI都可以用此种方式处理
2.6 反射和游戏逻辑
反射: 为了保证代码的扩展性而生,在代码和工具之间构建一个桥梁
Mustache:
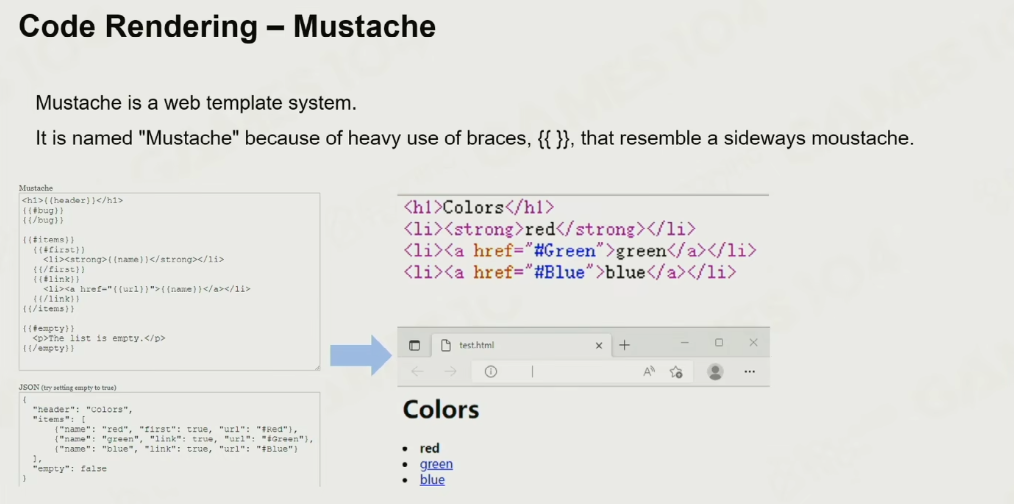
piccolo引擎的反射实现:
使用clang,并结合Mustache的Code Rendering技术批量生成代码
- 调用clang生成内存中的schema
- 根据写好的模板,调用 Mustache生成大量的accessable code
2.7 协同编辑
协同最大的问题就是解决冲突
-
分层的方法
优点当然是把复杂的场景进行细化, 但缺点是在于强关联的多层工作,无法更好的处理 -
对世界进行划分
优点是易于扩展一个世界,更好处理,缺点是对于跨世界的物体难处理 -
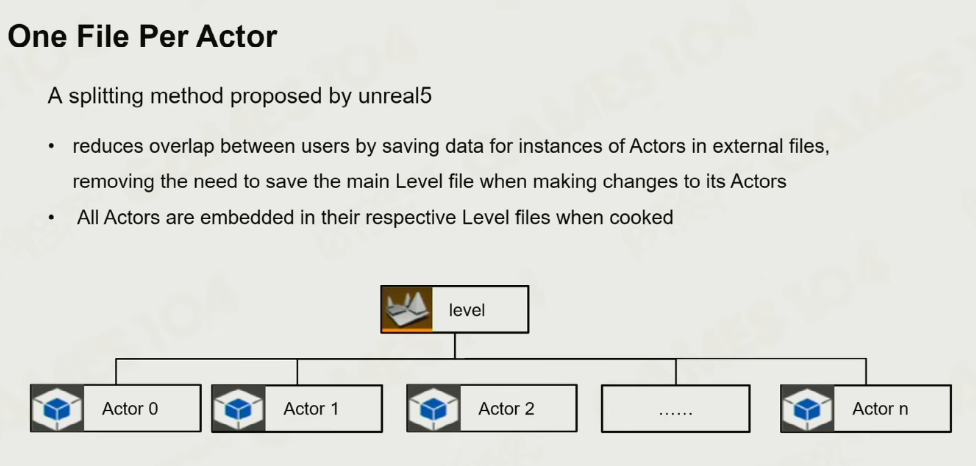
OFPA的方式
优点: 较彻底地解决冲突问题
问题是产生较多的小问题,把OFPA文件整合到level中时整个cook的过程会比较慢
协同的另一个问题: 同步问题
-
操作锁
-
资源锁
-
以上两种并不能解决undo redo的情况:
解决方案1:基于Operation Transform(OT)的方法
解决方案2: Conflict-free Replicated Data Type(CRDT)
协同的问题: 竞争问题
两种方案,更建议第二种,将结果先结算完再发到终端
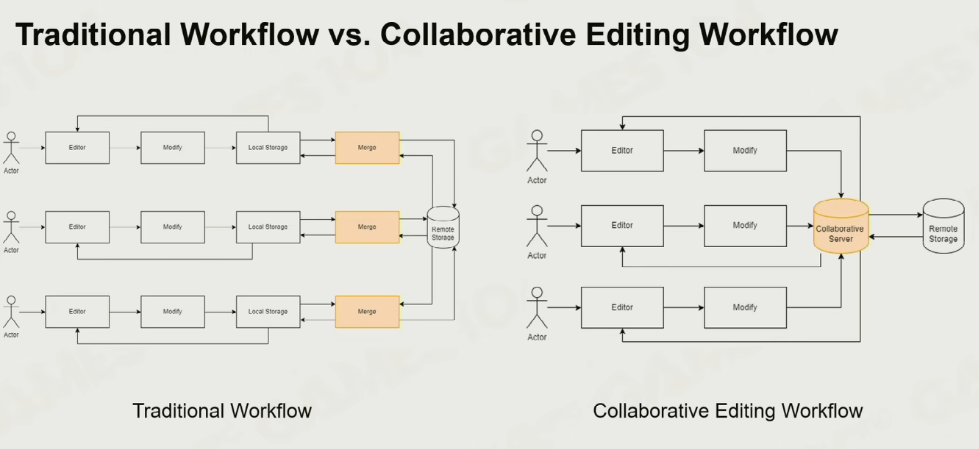
但这里有个隐患就是,这里的终端server需要保证稳定