GAMES101作业笔记
一、作业1
要求:
每次作业的评分,分为基础与提高两部分,即在作业批改时会给大家反馈两
个成绩。由于作业不是强制要求必须提交,所以在完成全部作业后,我们会统计
所有的基础分数。若基础分数及格则视为通过课程,反之视为不通过。
• [5 分] 正确构建模型矩阵。
• [5 分] 正确构建透视投影矩阵。
• [10 分] 你的代码可以在现有框架下正确运行,并能看到变换后的三角形。
• [10 分] 当按A 键与D 键时,三角形能正确旋转。或者正确使用命令行得
到旋转结果图像。
• [提高项5 分] 在main.cpp 中构造一个函数,该函数的作用是得到绕任意
过原点的轴的旋转变换矩阵。
Eigen::Matrix4f get_rotation(Vector3f axis, float angle)
//实现: |
二、作业2
要求
• [5 分] 正确地提交所有必须的文件,且代码能够编译运行。
• [20 分] 正确实现三角形栅格化算法。
• [10 分] 正确测试点是否在三角形内。
• [10 分] 正确实现z-buffer 算法, 将三角形按顺序画在屏幕上。
• [提高项5 分] 用super-sampling 处理Anti-aliasing : 你可能会注意
到,当我们放大图像时,图像边缘会有锯齿感。我们可以用super-sampling
来解决这个问题,即对每个像素进行2 * 2 采样,并比较前后的结果(这里
并不需要考虑像素与像素间的样本复用)。需要注意的点有,对于像素内的每
一个样本都需要维护它自己的深度值,即每一个像素都需要维护一个sample
list。最后,如果你实现正确的话,你得到的三角形不应该有不正常的黑边。
static bool insideTriangle(float x, float y, const Vector3f* _v) |
三、作业3
要求:
• [5 分] 提交格式正确,包括所有需要的文件。代码可以正常编译、执行。
• [10 分] 参数插值: 正确插值颜色、法向量、纹理坐标、位置(Shading Position)
并将它们传递给fragment_shader_payload.
• [20 分]Blinn-phong 反射模型: 正确实现phong_fragment_shader 对应的
反射模型。
• [5 分] Texture mapping: 将phong_fragment_shader 的代码拷贝到
texture_fragment_shader, 在此基础上正确实现Texture Mapping.
• [10 分] Bump mapping 与Displacement mapping: 正确实现Bump mapping
与Displacement mapping.
7
• [Bonus 3 分] 尝试更多模型: 找到其他可用的.obj 文件,提交渲染结果并
把模型保存在/models 目录下。这些模型也应该包含Vertex Normal 信息。
• [Bonus 5 分] 双线性纹理插值: 使用双线性插值进行纹理采样, 在Texture
类中实现一个新方法Vector3f getColorBilinear(float u, float v) 并
通过fragment shader 调用它。为了使双线性插值的效果更加明显,你应该
考虑选择更小的纹理图。请同时提交纹理插值与双线性纹理插值的结果,并
进行比较。
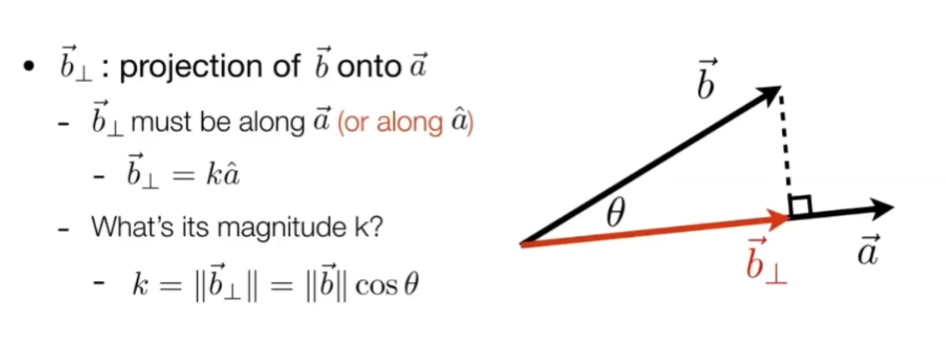
向量点积对应到矩阵的点乘,是对应项的相乘之和。 向量叉乘对应矩阵间的m行与n列对应相乘之和成为新的m,n项(矩阵相乘),结果是一个新矩阵
Eigen库的cwiseProduct实现了矩阵点积,即对应项相乘得到新的项,要求两个矩阵行列数要一样!
- rasterizer.cpp
//Screen space rasterization |
- Texture.hpp
Eigen::Vector3f getColor(float u, float v) |
- main.cpp - texture_fragment
Eigen::Vector3f texture_fragment_shader(const fragment_shader_payload& payload) |
- main.cpp - phong_fragment
Eigen::Vector3f phong_fragment_shader(const fragment_shader_payload& payload) |
- main.cpp - phong_fragment
Eigen::Vector3f displacement_fragment_shader(const fragment_shader_payload& payload) |
- main.cpp - bump_fragment
Eigen::Vector3f bump_fragment_shader(const fragment_shader_payload& payload) |
四、作业4
需要实现 de Casteljau 算法来绘制由 4 个控制点表示的 Bézier 曲线 (当你正确实现该
算法时,你可以支持绘制由更多点来控制的 Bézier 曲线)。
你需要修改的函数在提供的 main.cpp 文件中。
• bezier:该函数实现绘制 Bézier 曲线的功能。它使用一个控制点序列和一个
OpenCV::Mat 对象作为输入,没有返回值。它会使 t 在 0 到 1 的范围内进
行迭代,并在每次迭代中使 t 增加一个微小值。对于每个需要计算的 t,将
调用另一个函数 recursive_bezier,然后该函数将返回在 Bézier 曲线上 t
处的点。最后,将返回的点绘制在 OpenCV ::Mat 对象上。
• recursive_bezier:该函数使用一个控制点序列和一个浮点数 t 作为输入,
实现 de Casteljau 算法来返回 Bézier 曲线上对应点的坐标。
要求:
• [20 分] De Casteljau 算法:
对于给定的控制点,你的代码能够产生正确的 Bézier 曲线。
• [5 分] 奖励分数:
实现对 Bézier 曲线的反走样。(对于一个曲线上的点,不只把它对应于一个像
素,你需要根据到像素中心的距离来考虑与它相邻的像素的颜色。)
可能会有的问题:需要对每一个点进行差值
cv::Point2f recursive_bezier(const std::vector<cv::Point2f>& control_points, float t) |
五、作业5
需要修改的函数是:
• Renderer.cpp 中的 Render():这里你需要为每个像素生成一条对应的光
线,然后调用函数 castRay() 来得到颜色,最后将颜色存储在帧缓冲区的相
应像素中。
• Triangle.hpp 中的 rayTriangleIntersect(): v0, v1, v2 是三角形的三个
顶点,orig 是光线的起点,dir 是光线单位化的方向向量。tnear, u, v 是你需
要使用我们课上推导的 Moller-Trumbore 算法来更新的参数。
Renderer.cpp的推导:
- 将i,y 的屏幕坐标转成左下角为0,1的且以中心点0.5摆放
- 将坐标系转成中心为(0,1)范围
- 转为方形
- 关联上fov
- y轴需要反过来!
- 小蓝点异常? 将宽高-1
void Renderer::Render(const Scene& scene) |
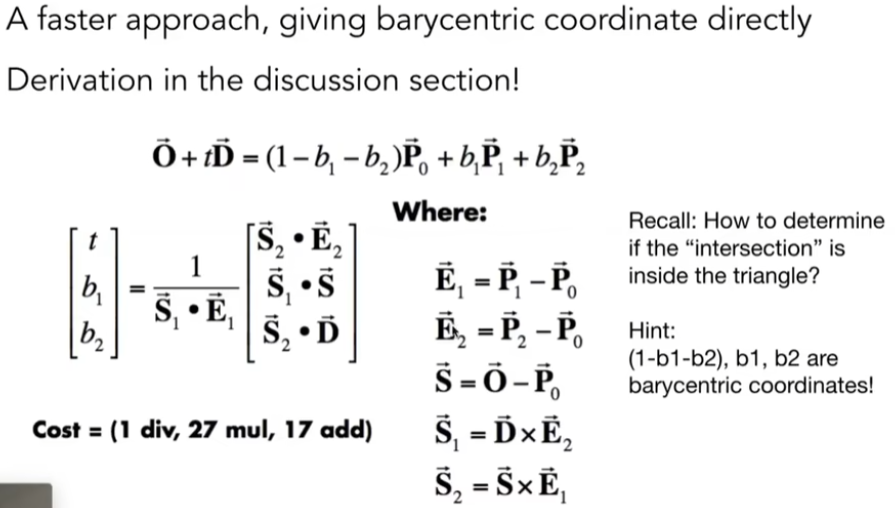
Moller Trumbore 算法来求光线是否在与平面有交点,使用重点坐标
|
生成的Ppm需要用此工具打开 https://www.fosshub.com/IrfanView.html?dwl=iview460_x64_setup.exe
六、作业6
本练习要求你实现 Ray-Bounding
Volume 求交与 BVH 查找。
首先,你需要从上一次编程练习中引用以下函数:
• Render() in Renderer.cpp: 将你的光线生成过程粘贴到此处,并且按照新框
架更新相应调用的格式。
• Triangle::getIntersection in Triangle.hpp: 将你的光线-三角形相交函数
粘贴到此处,并且按照新框架更新相应相交信息的格式。
在本次编程练习中,你需要实现以下函数:
• IntersectP(const Ray& ray, const Vector3f& invDir,
const std::array<int, 3>& dirIsNeg) in the Bounds3.hpp: 这个函数的
作用是判断包围盒 BoundingBox 与光线是否相交,你需要按照课程介绍的算
法实现求交过程。
• getIntersection(BVHBuildNode* node, const Ray ray)in BVH.cpp: 建
立 BVH 之后,我们可以用它加速求交过程。该过程递归进行,你将在其中调
用你实现的 Bounds3::IntersectP.
inline Intersection Triangle::getIntersection(Ray ray) |
SAH的方式: 参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/coolwx/p/14375763.html
BVHBuildNode* BVHAccel::recursiveBuild(std::vector<Object*>objects) |
SAH的方式,精髓在于把一个轴向分成一定数量的桶,在把所有物体根据重心坐标的偏移分到这些桶里,再用公式找到以哪个桶为中心时COST最低。 这是一个轴的,再将另外几个轴按相同算法算出。最后取最划算的轴和最划算的中心位置桶,得出最终的高效的BVH结构。
课件的例子中,如果使用NAIVE方法,构建自然更快,但最终render时会慢。对于更复杂的场景,SAH的效果将会更好。
七、作业7
路径追踪
本次实验中,你只需要修改这一个函数:
• castRay(const Ray ray, int depth)in Scene.cpp: 在其中实现 Path Tracing 算法
可能用到的函数有:
• intersect(const Ray ray)in Scene.cpp: 求一条光线与场景的交点
• sampleLight(Intersection pos, float pdf) in Scene.cpp: 在场景的所有
光源上按面积 uniform 地 sample 一个点,并计算该 sample 的概率密度
3
• sample(const Vector3f wi, const Vector3f N) in Material.cpp: 按照该
材质的性质,给定入射方向与法向量,用某种分布采样一个出射方向
• pdf(const Vector3f wi, const Vector3f wo, const Vector3f N) in Material.cpp: 给定一对入射、出射方向与法向量,计算 sample 方法得到该出射
方向的概率密度
• eval(const Vector3f wi, const Vector3f wo, const Vector3f N) in Material.cpp: 给定一对入射、出射方向与法向量,计算这种情况下的 f_r 值
可能用到的变量有:
• RussianRoulette in Scene.cpp: P_RR, Russian Roulette 的概率


参考: https://www.bilibili.com/read/cv12184818/
// IntersectionP的实现,正确的方式 |