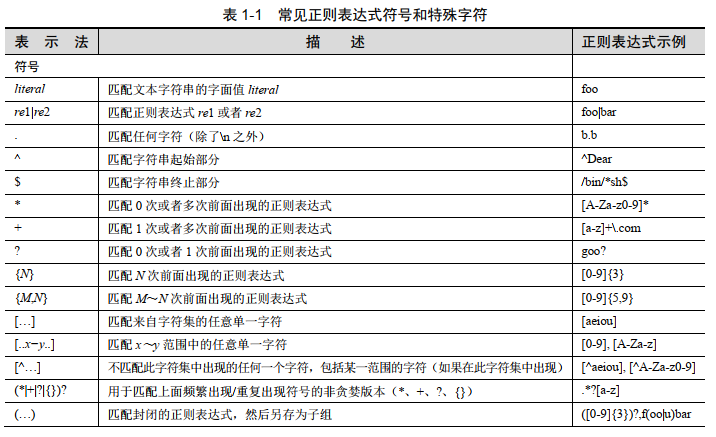
Python源码剖析-Note2
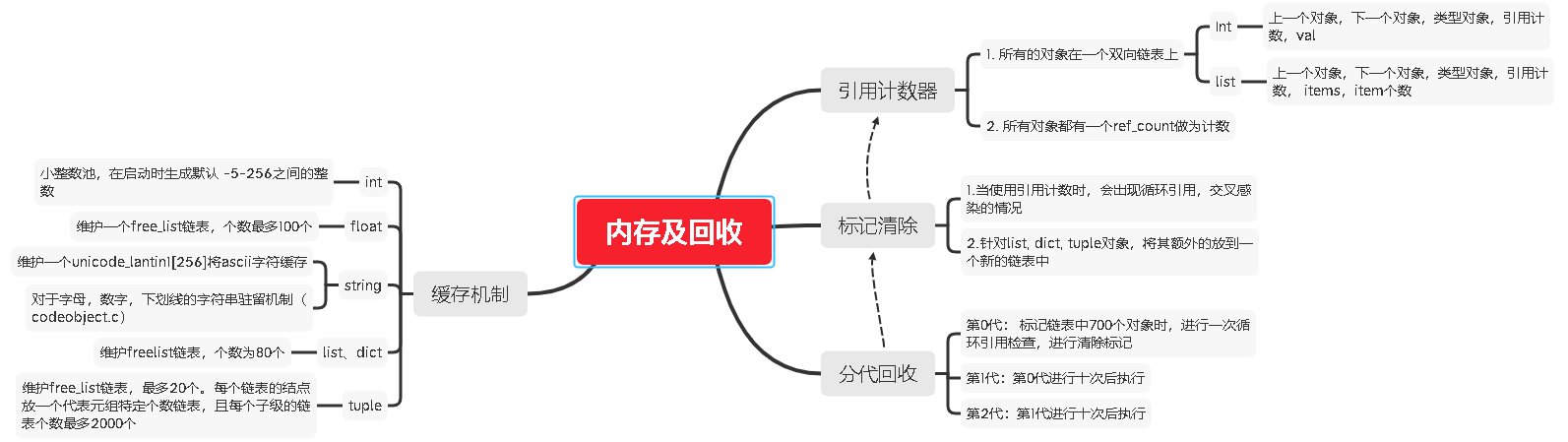
Python的内存
引用计数
由源码可知,Python的数据对象由PyVarObject(PyObject+size)组成,PyObject中又包含了双向链表,计数器,数据类型_typeobject对象(其中可以定制行为)
/* Define pointers to support a doubly-linked list of all live heap objects. */ |
标记清除
对于list, dict, tuple 这种类型,有可能存在循环引用的情况,这时需要再做一次扫描及标记清除的处理。
- 在Python中使用另一个新的链表来存储需要标记清除的对象。然而这种扫描的往往比较耗时,需要执行可达性分析,以找到unreachable的对象,对这些对象进行标记清除。
- 因此为标记清除的处理需要找一个时间点来。 这就引入了分代机制
分代机制
标记清除的扫描的操作比较耗时。所以需要设置一个时间点。
- Python中设置第一代为 700个对象, 第二代为第一代的10次,第三代为第二代的10次
- 可使用python的gc模块,从业务层对这些值进行设置
缓存机制
一、int的缓存机制
二、字符串的缓存机制:
-
intern dict : PyDict对象,key, value就是字符串
-
nullstring, characters, 空串和单串,有两个属性来存储
intern的默认识别只能在compile时,无法在runtime时识别,不过可以手动调用intern

三、tuple的缓存机制
PyTupleObject, 维护一个链表,用free_list存储链表头, 20个
不用像int和string一整块的申请,利用链表的ob_item组起来
四、list的缓存机制
维护一个free_list , 保存80个,运行时往里回放。
四、源码分析
obmalloc.c -> PyObject_Malloc
-
申请大小大于256,直接使用 PyMem_Malloc
-
小于256, 进入小块内存池
- 取size, 指定大小-1 后 除以8或者16字节。(设定一个block大小)
总结
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来源 Avery的城堡!